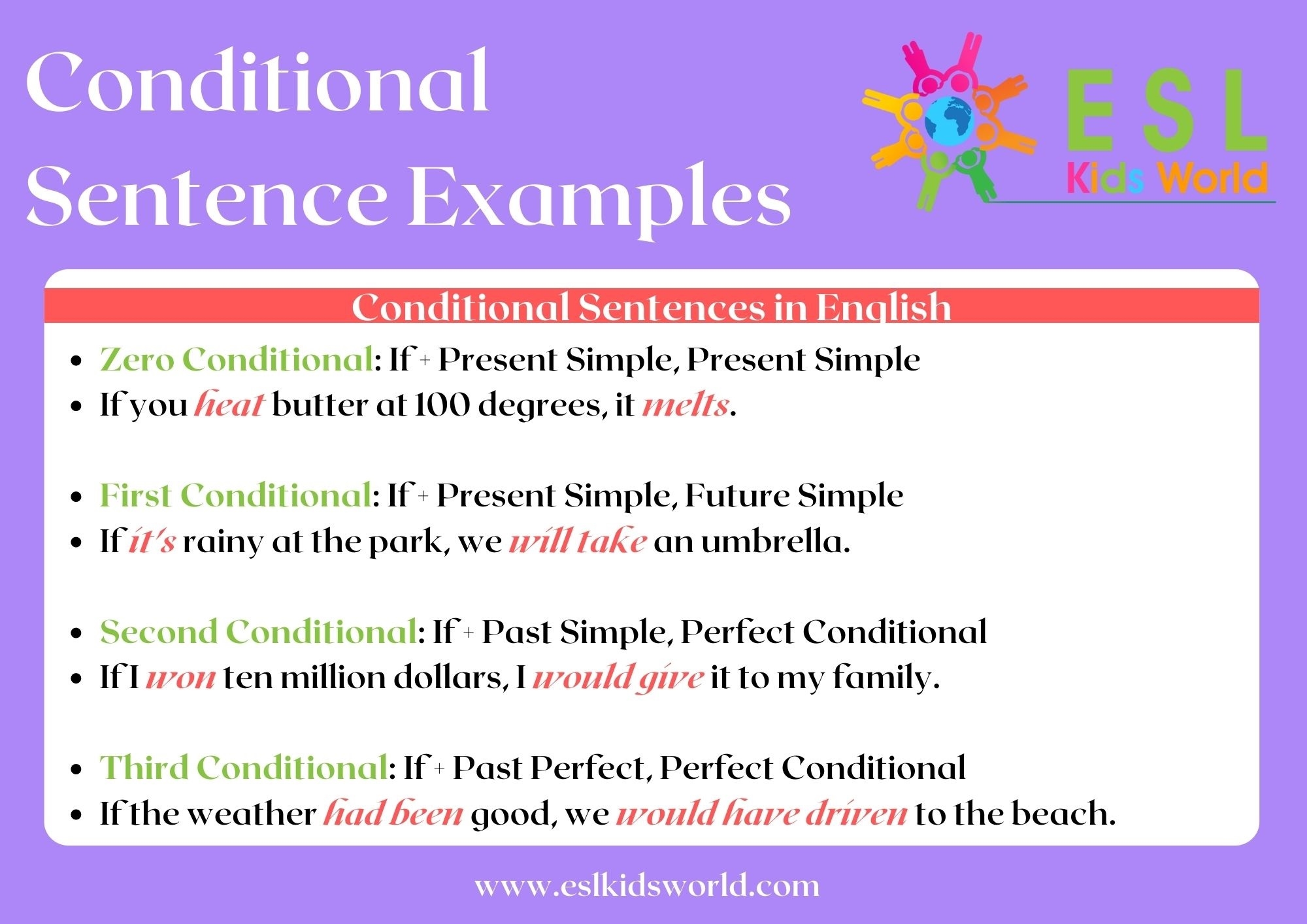
Conditional sentences are used to express hypothetical situations and their potential outcomes. They are structured in a way that conveys a dependency between two events. There are various types of conditional sentences, each serving a different purpose in communication. Understanding these types can help you effectively convey your thoughts and ideas.
Let’s explore three types of conditional sentences:
1. First Conditional
The first conditional is used to talk about future possibilities and their likely outcomes. It consists of two clauses – the if-clause and the main clause. The if-clause expresses a condition that must be met for the main clause to happen. For example, “If it rains tomorrow, I will bring an umbrella.” In this sentence, the condition (rain) is linked to the consequence (bringing an umbrella).
First conditionals are often used to make predictions or suggestions based on a specific condition. They are structured in a way that implies a high probability of the event happening.
2. Second Conditional
The second conditional is used to talk about hypothetical situations in the present or future. It is often used to express unreal or unlikely possibilities. The if-clause in second conditionals is in the past tense, while the main clause is in the conditional mood (would + base form of the verb).
For example, “If I won the lottery, I would travel the world.” In this sentence, the speaker is imagining a scenario that is unlikely to happen but is expressing what they would do if it did.
Second conditionals are commonly used in conversations about dreams, desires, or hypothetical scenarios that are not expected to become a reality.
3. Third Conditional
The third conditional is used to talk about hypothetical situations in the past. It is used to express situations that did not happen and their imagined outcomes. Both clauses in third conditionals are in the past perfect tense, and the main clause is in the conditional perfect tense (would have + past participle).
For example, “If I had studied harder, I would have passed the exam.” In this sentence, the speaker is reflecting on a past event (not studying hard) and imagining a different outcome if they had acted differently.
Third conditionals are often used to express regret, hindsight, or reflection on past events that could have had different outcomes under different circumstances.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of conditional sentences can enhance your ability to communicate effectively and convey complex ideas. By mastering the nuances of each type, you can express a range of possibilities, from likely outcomes to hypothetical scenarios and reflections on the past.