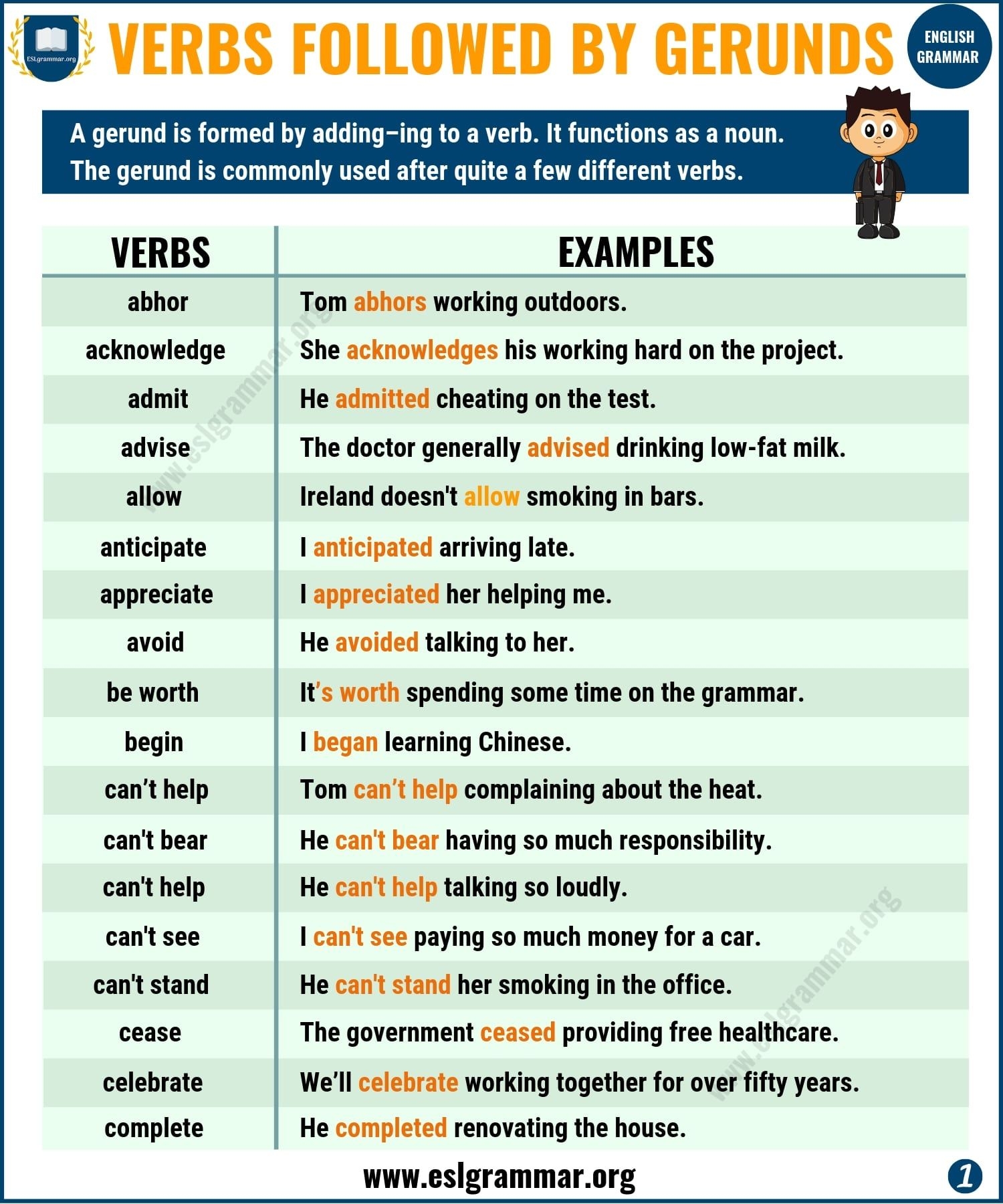
Gerunds are an essential part of the English language, often used in various forms of writing and speech. Understanding what gerunds are and how they function can greatly improve your grasp of grammar and communication skills.
A gerund is a verb form that functions as a noun in a sentence. It is created by adding the suffix “-ing” to a verb. Gerunds can be used in various ways, such as the subject of a sentence, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition.
Gerund Definition
Gerunds act as nouns but are derived from verbs. They are used to express actions or states in a more general sense, rather than as a specific action performed by a particular person or thing. For example, in the sentence “Swimming is her favorite hobby,” the word “swimming” is a gerund acting as the subject of the sentence.
Gerunds can also be used after certain verbs, such as enjoy, dislike, and appreciate. For example, “She enjoys reading books” uses the gerund “reading” as the object of the verb “enjoys.” In this case, the gerund functions as a noun, representing the activity that the subject enjoys.
Furthermore, gerunds can be used after prepositions to show the relationship between the gerund and other words in the sentence. For example, “I am interested in learning new languages” uses the gerund “learning” after the preposition “in,” indicating the subject’s interest in acquiring new languages.
It is important to note that gerunds can be confused with present participles, which also end in “-ing.” However, gerunds function as nouns, while present participles function as adjectives or as part of a verb tense. Differentiating between the two can help clarify the meaning of a sentence and improve overall comprehension.
In conclusion, gerunds play a crucial role in the English language, serving as versatile tools for expressing actions and states in various contexts. By understanding the definition and usage of gerunds, you can enhance your writing and communication skills, making your language more precise and engaging.