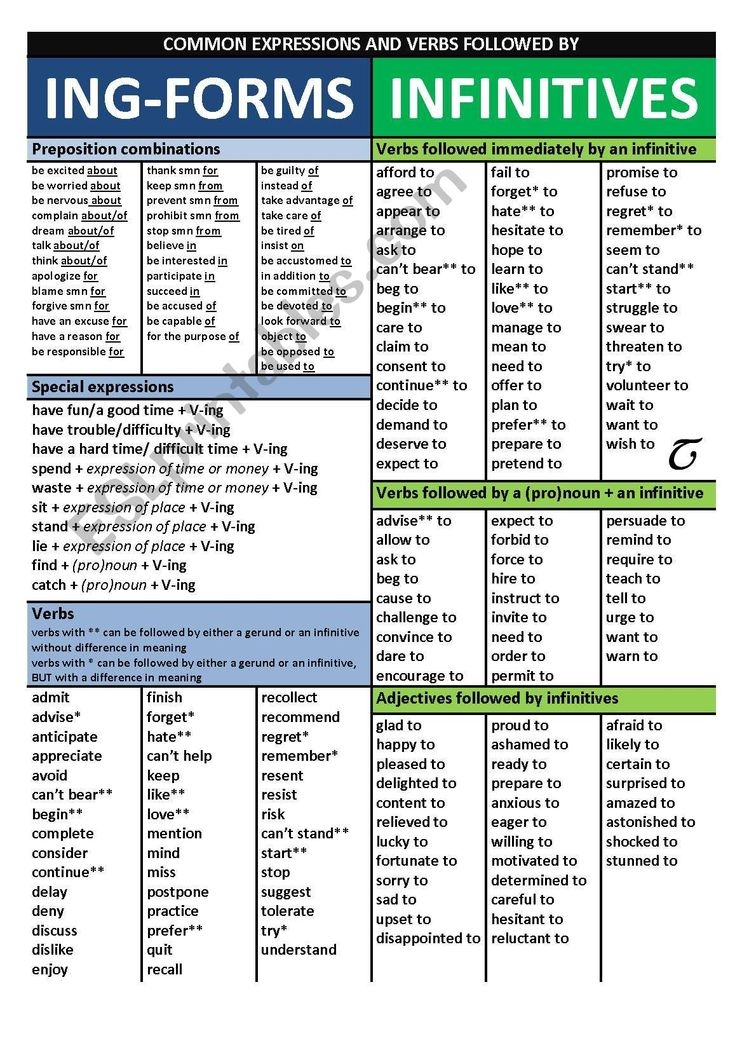
Gerunds and infinitives are verb forms that can function as nouns in a sentence. They are commonly used in English grammar to express actions or states of being. Understanding when to use gerunds and infinitives can help improve your overall language skills.
Gerunds are formed by adding -ing to a verb, while infinitives are the base form of a verb preceded by ‘to’. Knowing the difference between these two forms can be crucial in constructing grammatically correct sentences.
Gerunds and Infinitives:
- Gerunds: running, swimming, reading, cooking, singing
- Infinitives: to run, to swim, to read, to cook, to sing
1. Gerunds can be used as subjects of sentences, as in “Running is good exercise.” They can also function as objects of verbs, as in “She enjoys swimming in the ocean.”
2. Infinitives are often used after certain verbs like ‘want’, ‘need’, ‘like’, ‘plan’, etc. For example, “I want to learn how to play the guitar.” Infinitives can also follow adjectives, as in “It is important to be honest.”
3. Some verbs can be followed by both gerunds and infinitives, but with a change in meaning. For example, “I remembered calling her” (I did the calling) vs. “I remembered to call her” (I remembered that I needed to call her).
4. Gerunds can be used after prepositions, as in “I am good at playing the piano.” Infinitives, on the other hand, are used after adjectives, as in “He is happy to help.”
Understanding the differences between gerunds and infinitives can make your English writing and speaking more precise and effective. Practice using these verb forms in various contexts to improve your language skills.
In conclusion, gerunds and infinitives are essential components of English grammar that can help convey actions and ideas in a sentence. By mastering the use of gerunds and infinitives, you can enhance your communication skills and express yourself more clearly.