Nouns are an essential part of language, serving as the building blocks for sentences. They are words that represent a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns can be common or proper, with proper nouns referring to specific names of people, places, or things.
Proper nouns are always capitalized, regardless of where they appear in a sentence. They provide specificity and help differentiate between similar entities. Understanding the difference between nouns and proper nouns is crucial for effective communication.
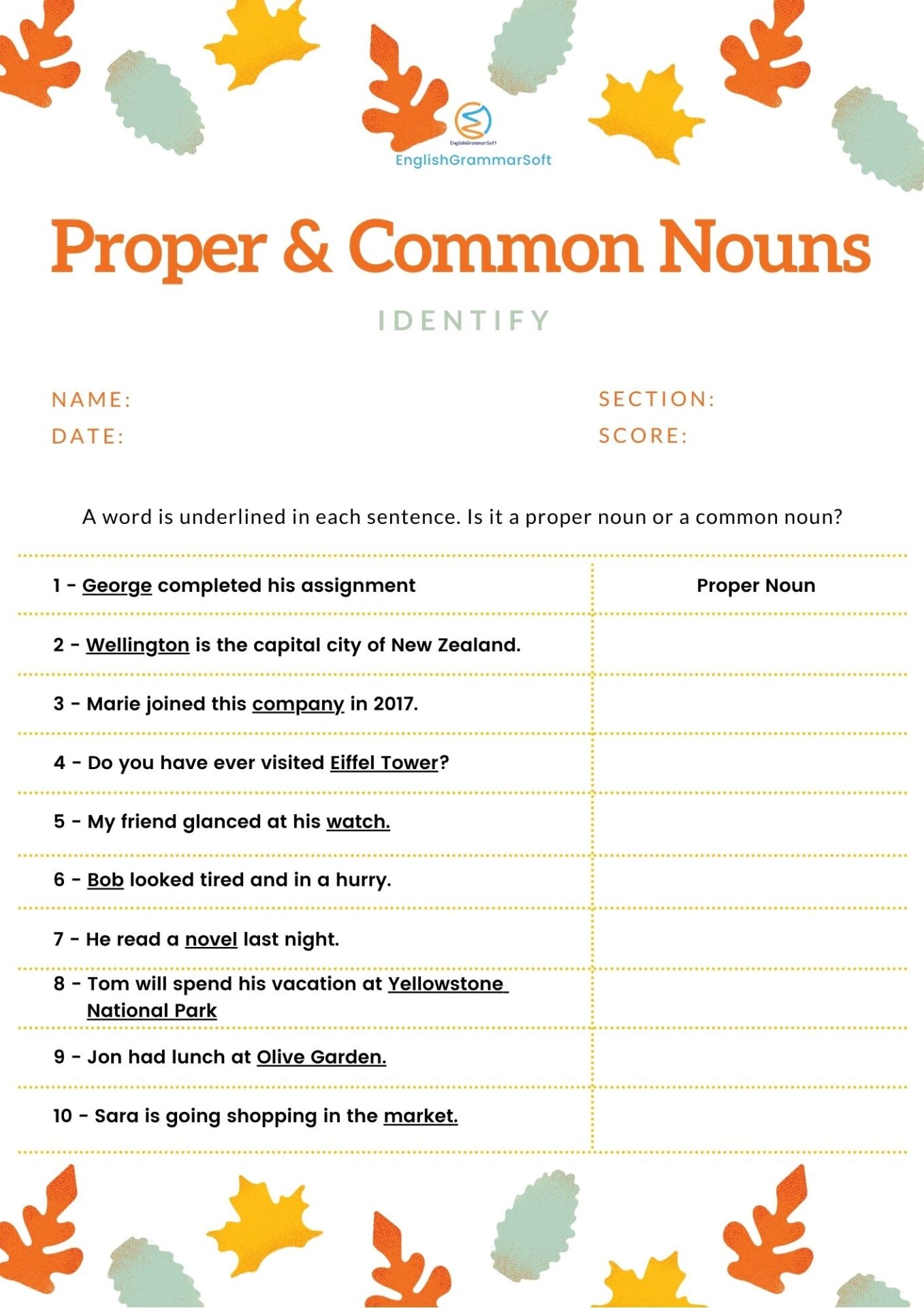
Noun and Proper Noun
Common nouns are general names for people, places, or things, such as “teacher,” “city,” or “book.” They are not capitalized unless they appear at the beginning of a sentence. Proper nouns, on the other hand, refer to specific names and are always capitalized. Examples of proper nouns include “Mary,” “Paris,” and “The Great Gatsby.”
Proper nouns are used to identify unique entities, while common nouns are more general and can refer to multiple instances. For example, “dog” is a common noun that can describe any canine, while “Lassie” is a proper noun that refers to a specific dog. Proper nouns add specificity and detail to language.
When writing, it is important to use proper nouns correctly to avoid confusion. By capitalizing names of people, places, and things, readers can easily identify the specific entities being referenced. Proper nouns help create a clear and concise communication, enhancing the overall quality of writing.
In conclusion, nouns and proper nouns play a crucial role in language by identifying and distinguishing entities. While common nouns are general names for people, places, or things, proper nouns refer to specific names that are always capitalized. Understanding the difference between the two is essential for effective communication and clear writing.