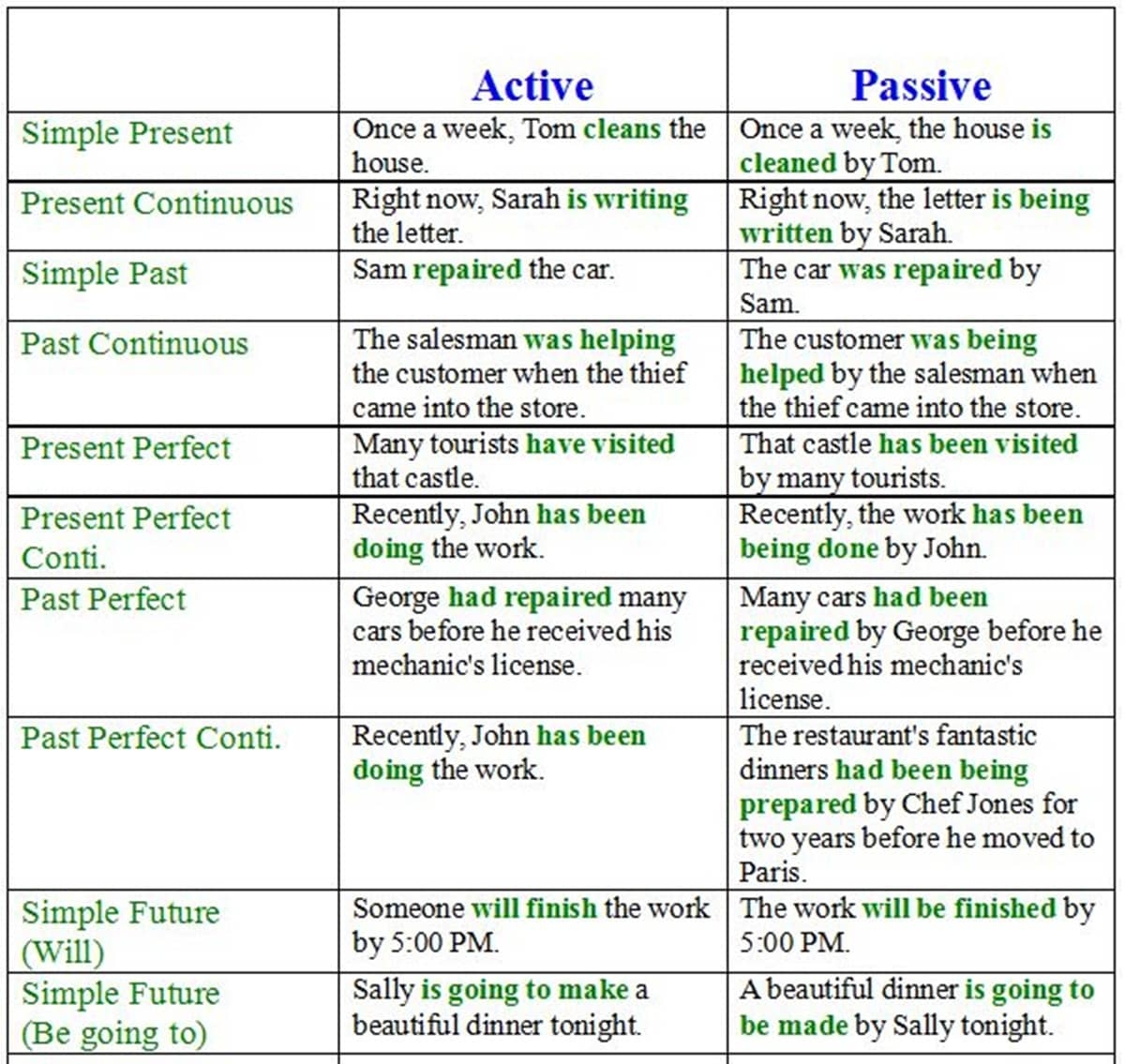
Having a strong grasp of English grammar is essential for effective communication and writing. It not only helps convey your message clearly but also enhances your credibility as a speaker or writer. One important aspect of English grammar that is often misunderstood or misused is the passive voice.
The passive voice is a grammatical construction where the subject of a sentence is the recipient of the action, rather than the doer. It is formed by using a form of the verb “to be” followed by the past participle of the main verb. For example, “The book was written by the author.” In this sentence, the book is the subject and the author is the doer of the action.
Using the passive voice can be useful in certain situations, such as when the doer of the action is unknown or unimportant, or when you want to focus on the action itself rather than the doer. However, overusing the passive voice can make your writing sound dull and impersonal. It is important to strike a balance and use the passive voice judiciously.
One common mistake people make with the passive voice is using it unnecessarily or incorrectly. It is important to remember that the passive voice should only be used when the focus of the sentence is on the action rather than the doer. For example, saying “The report was written by me” is unnecessarily wordy and can be simplified to “I wrote the report.”
Another common mistake is using passive constructions with transitive verbs that do not require a direct object. For example, saying “The car was driven” is incorrect because the verb “drive” requires a direct object (e.g. “The car was driven by John”). It is important to pay attention to the structure of the sentence and ensure that the passive voice is used correctly.
In conclusion, mastering the passive voice in English grammar can help enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your writing. By understanding when and how to use the passive voice correctly, you can improve the flow and coherence of your sentences. Remember to practice and experiment with different sentence structures to develop a strong command of the passive voice.