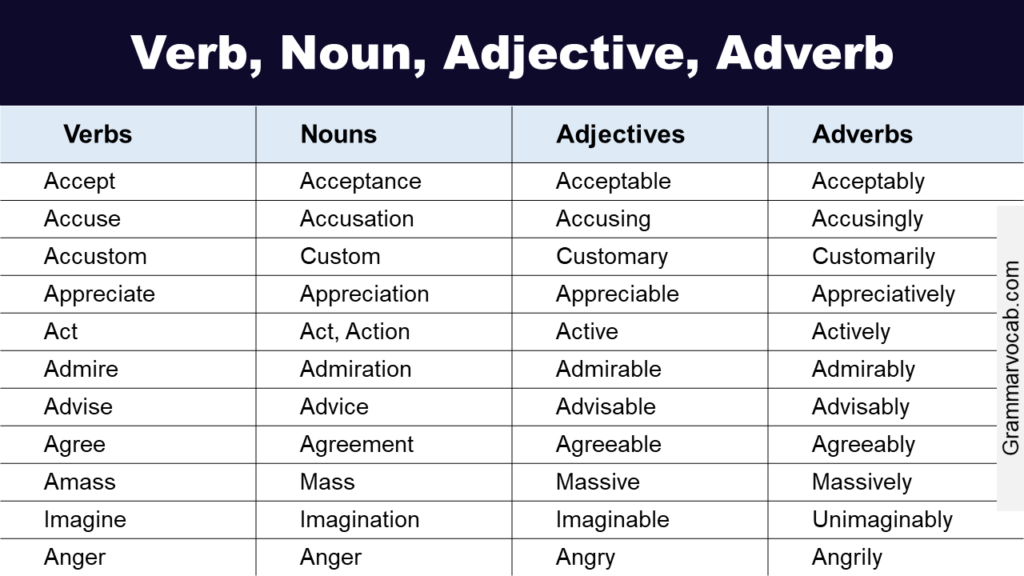
When it comes to describing words, adjectives and adverbs are commonly used in the English language. While they may seem similar, they serve different purposes in a sentence. Understanding the difference between adjectives and adverbs can help improve your writing skills and communication.
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They provide more information about the noun or pronoun by answering questions such as “What kind?” “Which one?” “How many?” or “How much?” For example, in the sentence “The cute puppy chased the ball,” the word “cute” is an adjective that describes the noun “puppy.”
Adjective vs Adverbs
On the other hand, adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They often answer questions such as “How?” “When?” “Where?” “To what extent?” or “Under what conditions?” For instance, in the sentence “She quickly ran to the store,” the word “quickly” is an adverb that modifies the verb “ran.”
One key difference between adjectives and adverbs is their placement in a sentence. Adjectives usually come before the noun they modify, while adverbs can appear before or after the verb. It’s important to use adjectives and adverbs correctly to convey the intended meaning and avoid confusion.
Another distinction between adjectives and adverbs is their comparative and superlative forms. Adjectives change form to indicate degrees of comparison, such as “big, bigger, biggest,” while adverbs often use “more” or “most” to show comparison, like “quickly, more quickly, most quickly.” Understanding these forms can help you accurately describe things in your writing.
In conclusion, adjectives and adverbs play essential roles in the English language by providing additional information and describing words in a sentence. By knowing the difference between adjectives and adverbs, you can enhance your writing skills and effectively communicate your ideas. Practice using both adjectives and adverbs in your sentences to improve your language proficiency and make your writing more engaging.