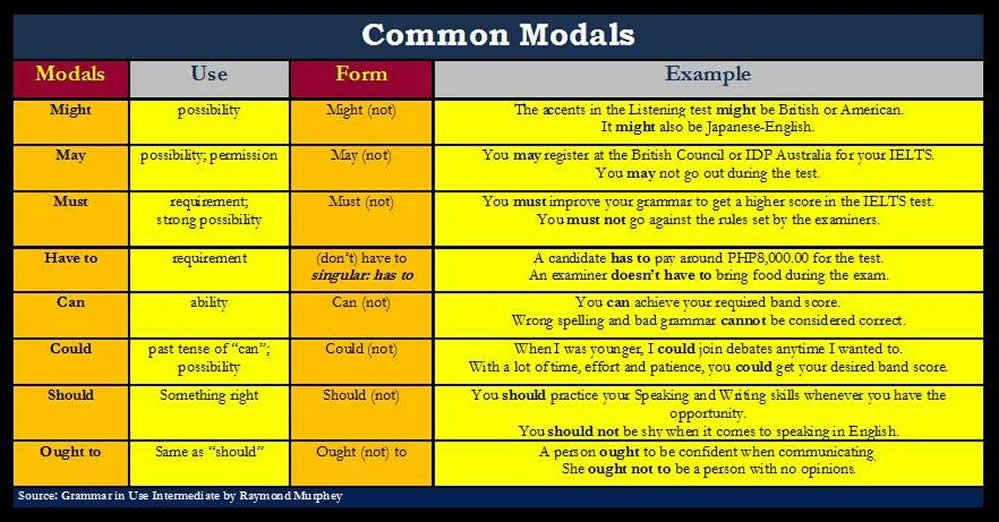
Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb that express necessity, possibility, ability, or permission. They are used to indicate the likelihood or necessity of an action or event. In English, modal verbs are followed by a base verb, and they do not change form based on the subject of the sentence.
Modal verbs play an important role in expressing various nuances in language, and understanding their usage can greatly enhance your communication skills. Here are some examples of modal verbs:
Examples of Modal Verbs
1. Can: Can is used to express ability or possibility. For example, “She can speak Spanish fluently.” This sentence indicates that she has the ability to speak Spanish.
2. Must: Must is used to express necessity or obligation. For example, “You must finish your homework before you go out.” This sentence indicates that finishing homework is necessary before going out.
3. Should: Should is used to give advice or make recommendations. For example, “You should eat more vegetables for better health.” This sentence suggests that eating more vegetables is a good idea.
4. May: May is used to express permission or possibility. For example, “May I borrow your pen?” This sentence asks for permission to borrow the pen.
5. Would: Would is used to indicate a polite request or a hypothetical situation. For example, “Would you mind closing the window?” This sentence is a polite way of asking someone to close the window.
Modal verbs are versatile and can convey various meanings depending on the context in which they are used. By mastering the usage of modal verbs, you can improve your ability to express yourself clearly and effectively in English.
Next time you are writing or speaking in English, try incorporating modal verbs to add depth and nuance to your communication. Whether you are expressing necessity, possibility, ability, or permission, modal verbs can help you convey your intended meaning with precision.