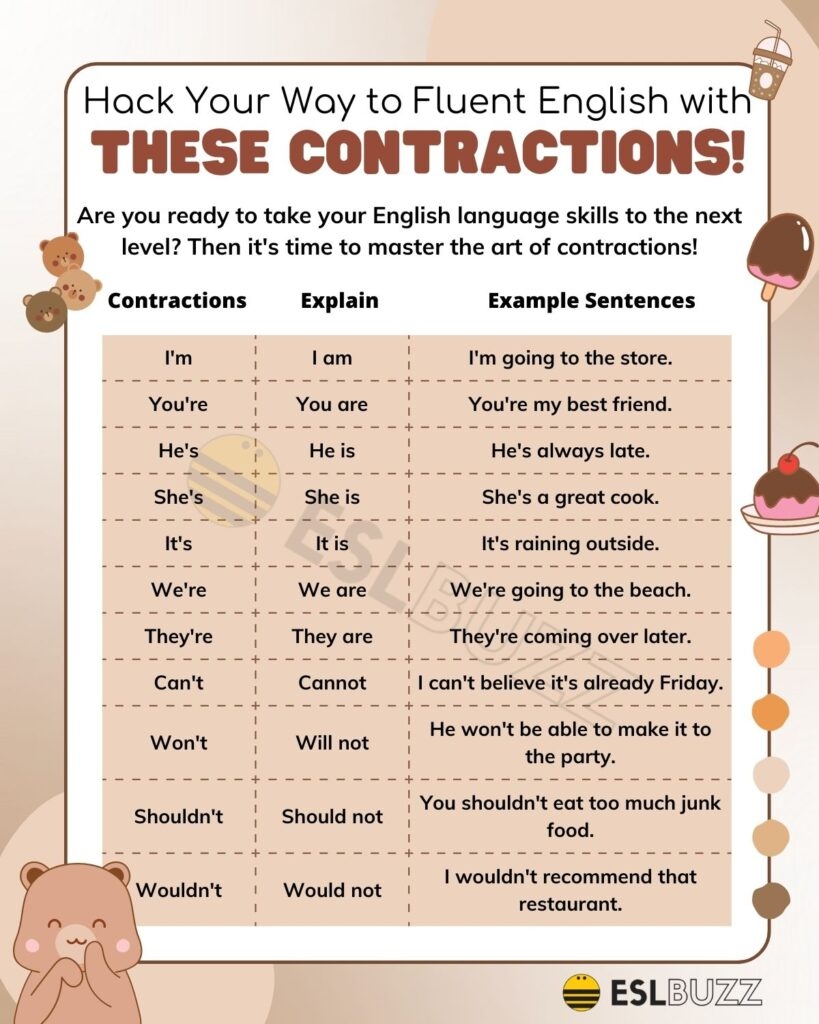
Contractions are shortened forms of words or phrases that are created by combining two words and omitting certain letters. They are commonly used in informal writing and speech to make communication more efficient. Knowing the complete list of contractions can help you improve your writing skills and understand informal language better.
Below is a comprehensive list of contractions that you may come across in everyday conversations and texts:
List of Contractions:
- I’m (I am)
- You’re (You are)
- He’s (He is)
- She’s (She is)
- We’re (We are)
- They’re (They are)
- It’s (It is)
- Can’t (Cannot)
- Don’t (Do not)
- Won’t (Will not)
- Shouldn’t (Should not)
- Isn’t (Is not)
- Wasn’t (Was not)
- Couldn’t (Could not)
Contractions are widely used in both spoken and written English to convey informality and efficiency. They can help to simplify language and make it more accessible to a wider audience. However, it is important to use contractions appropriately and be mindful of the context in which they are being used.
When using contractions in writing, it is essential to consider the tone and formality of the text. In formal writing, such as academic papers or business correspondence, it is generally best to avoid contractions and use the full forms of words instead. On the other hand, in informal writing, such as emails or text messages, contractions are perfectly acceptable and can help to convey a more conversational tone.
By familiarizing yourself with the complete list of contractions and understanding how they are used, you can enhance your language skills and communicate more effectively in a variety of settings. Practice using contractions in your writing and speech to become more comfortable with them and incorporate them seamlessly into your communication.
In conclusion, contractions play a significant role in the English language by providing a convenient way to shorten words and phrases. By learning the complete list of contractions and practicing their usage, you can improve your language skills and communicate more effectively in both formal and informal contexts.