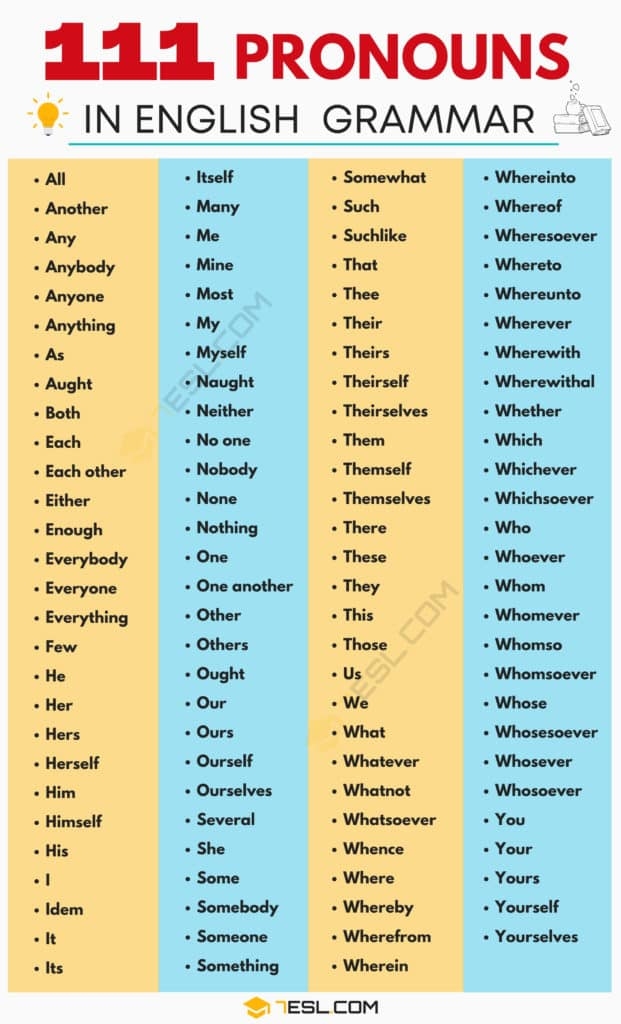
Pronouns are words that are used to replace nouns in a sentence. They help avoid repetition and make sentences more concise. Pronouns can refer to people, animals, things, or ideas. There are several different types of pronouns, each serving a specific purpose in communication.
In English grammar, pronouns can be categorized into personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, reflexive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, interrogative pronouns, relative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. Each type of pronoun has its own set of rules for usage and can vary based on the gender, number, and case of the noun it replaces.
List of Pronouns:
1. Personal Pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
2. Possessive Pronouns: mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs
3. Reflexive Pronouns: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
4. Demonstrative Pronouns: this, that, these, those
5. Interrogative Pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, what
Personal pronouns are used to refer to specific individuals or groups, while possessive pronouns indicate ownership or possession. Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and object of a sentence are the same, and demonstrative pronouns point to specific things or people. Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions about people or things.
Relative pronouns are used to introduce clauses in a sentence and connect them to the main idea. Indefinite pronouns do not refer to a specific person or thing and are more general in nature. Understanding the different types of pronouns and how to use them correctly is essential for effective communication in English.
In conclusion, pronouns play a crucial role in the English language by helping to streamline communication and make sentences more efficient. By using pronouns effectively, writers and speakers can avoid unnecessary repetition and convey their ideas more clearly. It is important to learn the rules for using pronouns correctly in order to communicate effectively in both written and spoken language.