Learning a new language can be both challenging and exciting. When it comes to the German language, one of the key components to master is the verb system. German verbs can be complex, but once you understand the basics, you’ll be able to communicate more effectively in German.
Verbs in German play a crucial role in constructing sentences and conveying actions. They indicate the action or state of being in a sentence. German verbs are conjugated based on the subject of the sentence, as well as the tense and mood of the verb.
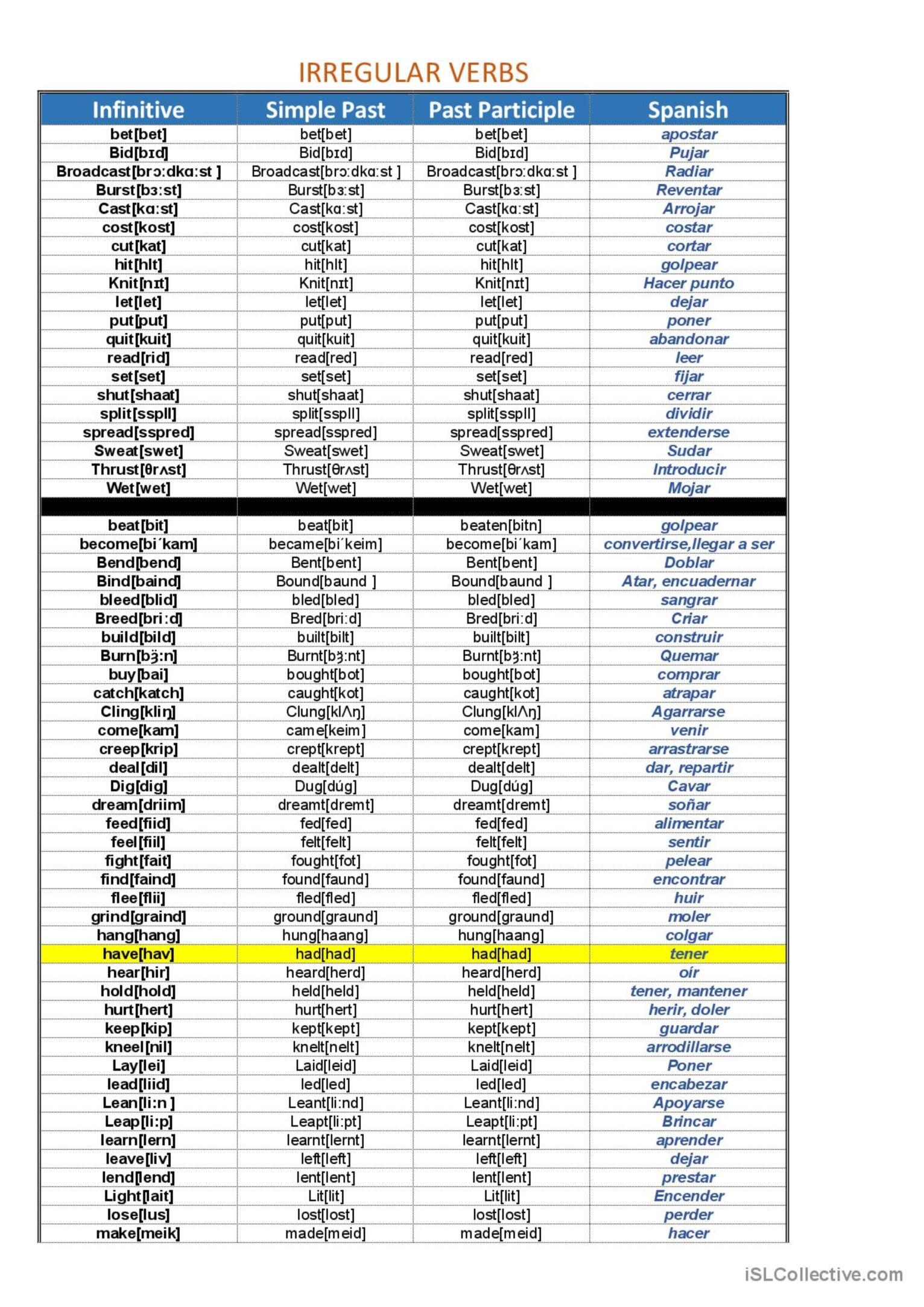
Deutsch Verbs
German verbs are categorized into strong verbs, weak verbs, and mixed verbs. Strong verbs undergo a vowel change in the past tense, while weak verbs form the past tense by adding a suffix. Mixed verbs exhibit characteristics of both strong and weak verbs.
It’s important to pay attention to the conjugation of German verbs based on the subject pronouns. These include ich (I), du (you), er/sie/es (he/she/it), wir (we), ihr (you plural), and sie/Sie (they/you formal). Each subject pronoun requires a different verb form.
Additionally, German verbs are also conjugated based on the tense and mood of the verb. There are several tenses in German, including present, past, future, and subjunctive. Each tense has its own conjugation rules that must be followed to ensure grammatical correctness.
Practice is key when it comes to mastering German verbs. The more you practice conjugating verbs and using them in context, the more comfortable you’ll become with the language. Reading, writing, and speaking in German regularly will help reinforce your understanding of verbs and improve your overall language skills.
In conclusion, German verbs are a fundamental aspect of the language that require time and effort to master. By understanding the different types of verbs, subject pronouns, tenses, and moods, you’ll be on your way to becoming more proficient in German. Keep practicing and don’t be afraid to make mistakes – it’s all part of the learning process!