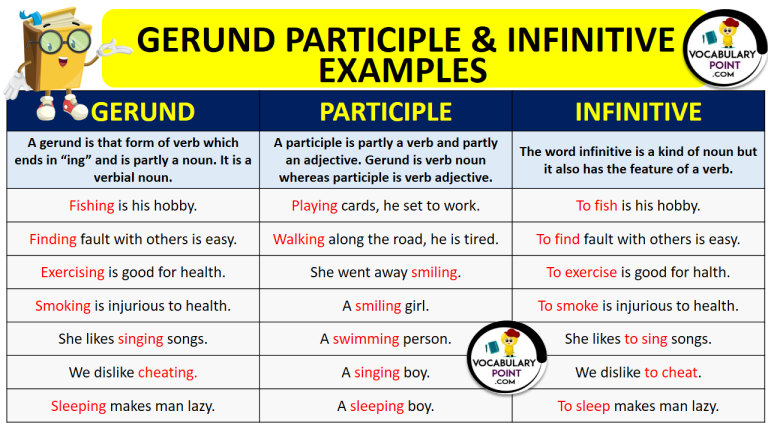
Understanding the differences between gerunds and infinitives is essential for mastering English grammar. Both gerunds and infinitives are forms of verbs that can act as nouns in a sentence, but they are used in different ways. Let’s explore the distinctions between these two forms to help you use them correctly in your writing and speaking.
Gerunds are verb forms that end in -ing and act as nouns in a sentence. They are used to describe an action or activity in a general sense. For example, “Swimming is my favorite hobby” – here, “swimming” is a gerund that functions as the subject of the sentence. Gerunds can also follow prepositions, such as in the sentence “I am good at dancing.”
Differences Between Gerund and Infinitive
Infinitives, on the other hand, are the base form of a verb preceded by the word “to.” They can also function as nouns in a sentence, but they are used in different contexts than gerunds. Infinitives are often used after certain verbs, such as “want,” “need,” or “prefer.” For example, “I want to travel the world” – here, “to travel” is an infinitive that follows the verb “want.”
One key difference between gerunds and infinitives is their ability to take direct objects. While gerunds can take direct objects, infinitives often require them. For example, “I enjoy reading books” (gerund with no direct object) versus “I want to read that book” (infinitive with a direct object). Understanding when to use a gerund or infinitive with a direct object is crucial for constructing clear and grammatically correct sentences.
Another distinction between gerunds and infinitives is their use with certain verbs. Some verbs can be followed by either a gerund or an infinitive, but the meaning can change depending on the form used. For example, “I remembered calling my friend” (gerund, indicating past action) versus “I remembered to call my friend” (infinitive, indicating intention or plan).
In conclusion, while gerunds and infinitives both function as nouns in a sentence, they have distinct uses and applications. Gerunds are verb forms ending in -ing that describe actions or activities, while infinitives are the base form of a verb preceded by “to” and often used after certain verbs. Understanding the differences between gerunds and infinitives will help you communicate effectively and accurately in English.