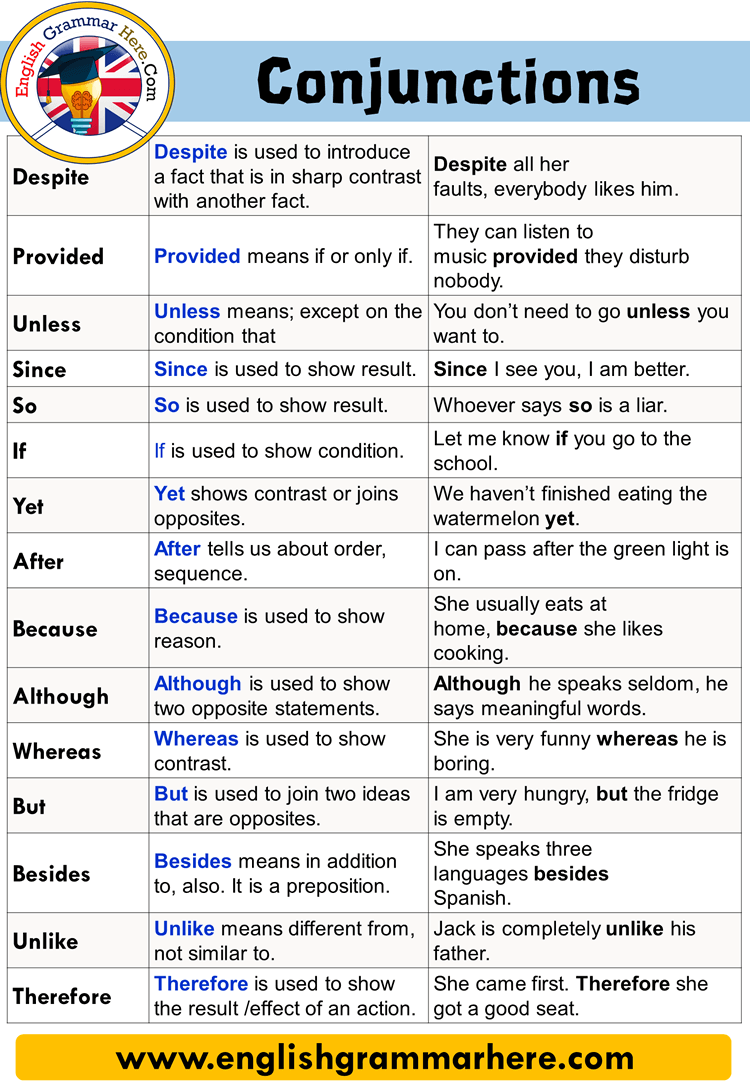
Conjunctions are an important part of grammar as they are used to connect words, phrases, or clauses. They help to create complex sentences and establish relationships between different parts of a sentence. There are three main types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions.
Coordinating conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance. Some common coordinating conjunctions include “and,” “but,” “or,” “nor,” “for,” “so,” and “yet.” For example, “I wanted to go to the movies, but I was too tired.”
Examples of Conjunctions:
Subordinating conjunctions are used to connect dependent clauses to independent clauses. They help to show the relationship between the two clauses, such as cause and effect, contrast, or time. Some common subordinating conjunctions include “because,” “although,” “while,” “if,” “since,” and “when.” For example, “I will go for a walk if the weather is nice.”
Correlative conjunctions are used in pairs to connect words, phrases, or clauses. Some common correlative conjunctions include “either…or,” “both…and,” “neither…nor,” “not only…but also,” and “whether…or.” For example, “She is both intelligent and hardworking.”
Conjunctions are essential in creating well-structured and coherent sentences. They help to establish the relationships between different parts of a sentence and make the text easier to read and understand. By using conjunctions effectively, you can create more complex and interesting sentences that convey your message clearly.
In conclusion, conjunctions play a vital role in grammar by connecting words, phrases, and clauses to form meaningful sentences. Whether it’s coordinating, subordinating, or correlative conjunctions, each type serves a specific purpose in creating well-structured sentences. By understanding and using conjunctions correctly, you can enhance the clarity and coherence of your writing.