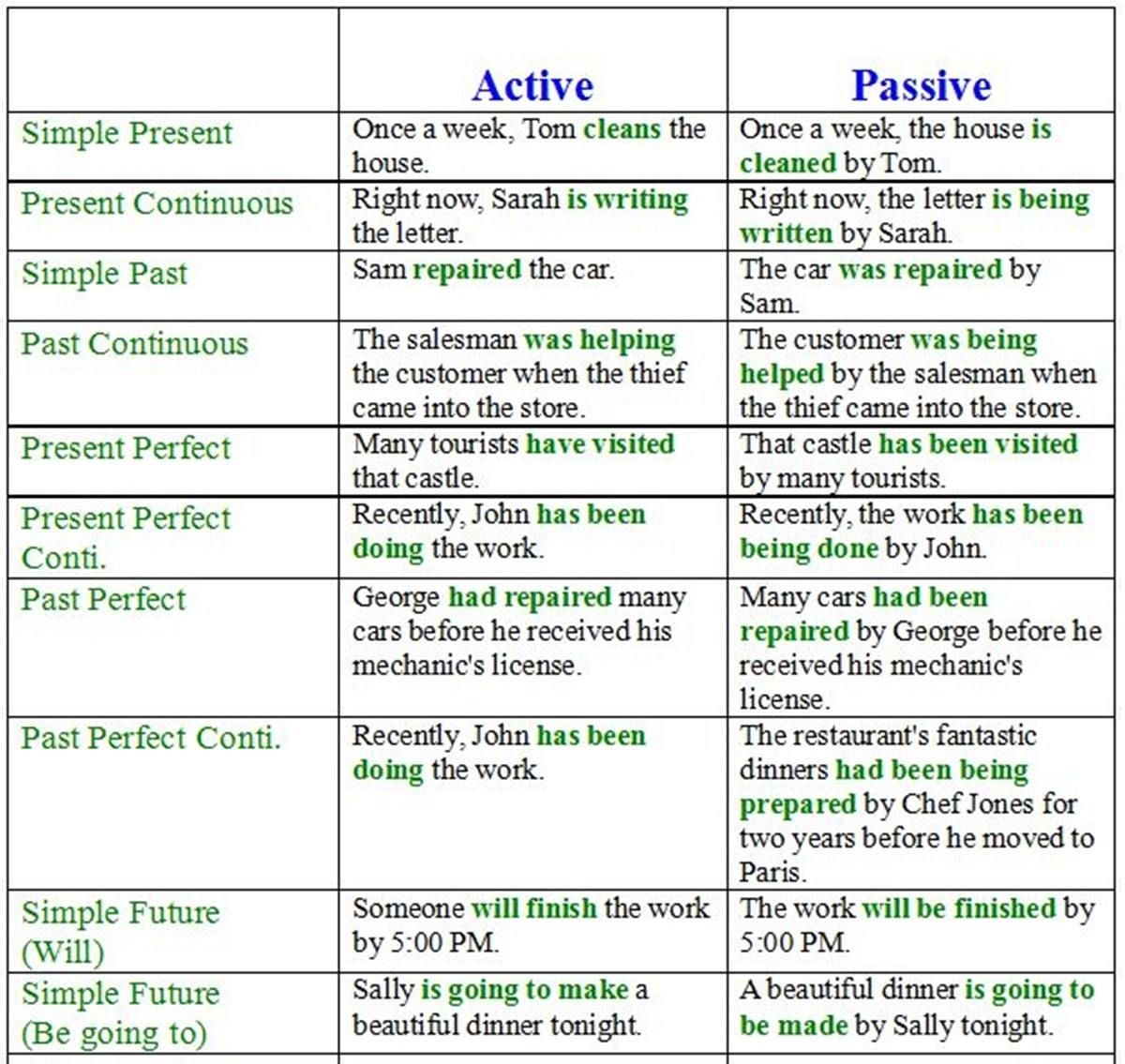
Passive sentences are sentences in which the subject of the sentence is acted upon by the verb. This means that the focus is on the receiver of the action rather than the doer. Passive sentences are often used in formal writing or when the doer of the action is unknown or unimportant. Here are some examples of passive sentences:
Passive sentences can be identified by the use of a form of “to be” (such as is, are, was, were) followed by a past participle. These sentences often lack a clear subject or have the subject placed after the verb. While passive sentences are not as direct as active sentences, they can be useful in certain contexts.
Examples of Passive Sentences:
1. The cake was baked by my sister.
2. The report will be submitted by the end of the week.
3. The book was read by millions of people.
4. The car was stolen last night.
5. The decision was made by the committee.
Passive sentences are commonly used in academic writing, scientific reports, and news articles. They can help to create a more formal tone and shift the focus to the receiver of the action. While passive sentences can be effective in certain situations, it is important to use them judiciously and consider the clarity and impact of the sentence.
It is also worth noting that passive sentences can sometimes make writing less engaging or dynamic. In some cases, using active sentences can help to make the writing more lively and direct. It is important to consider the context and purpose of the writing when deciding whether to use passive or active sentences.
In conclusion, passive sentences can be a useful tool in writing when used appropriately. They can help to shift the focus of the sentence and create a more formal tone. By understanding how to identify and use passive sentences effectively, writers can enhance the clarity and impact of their writing.