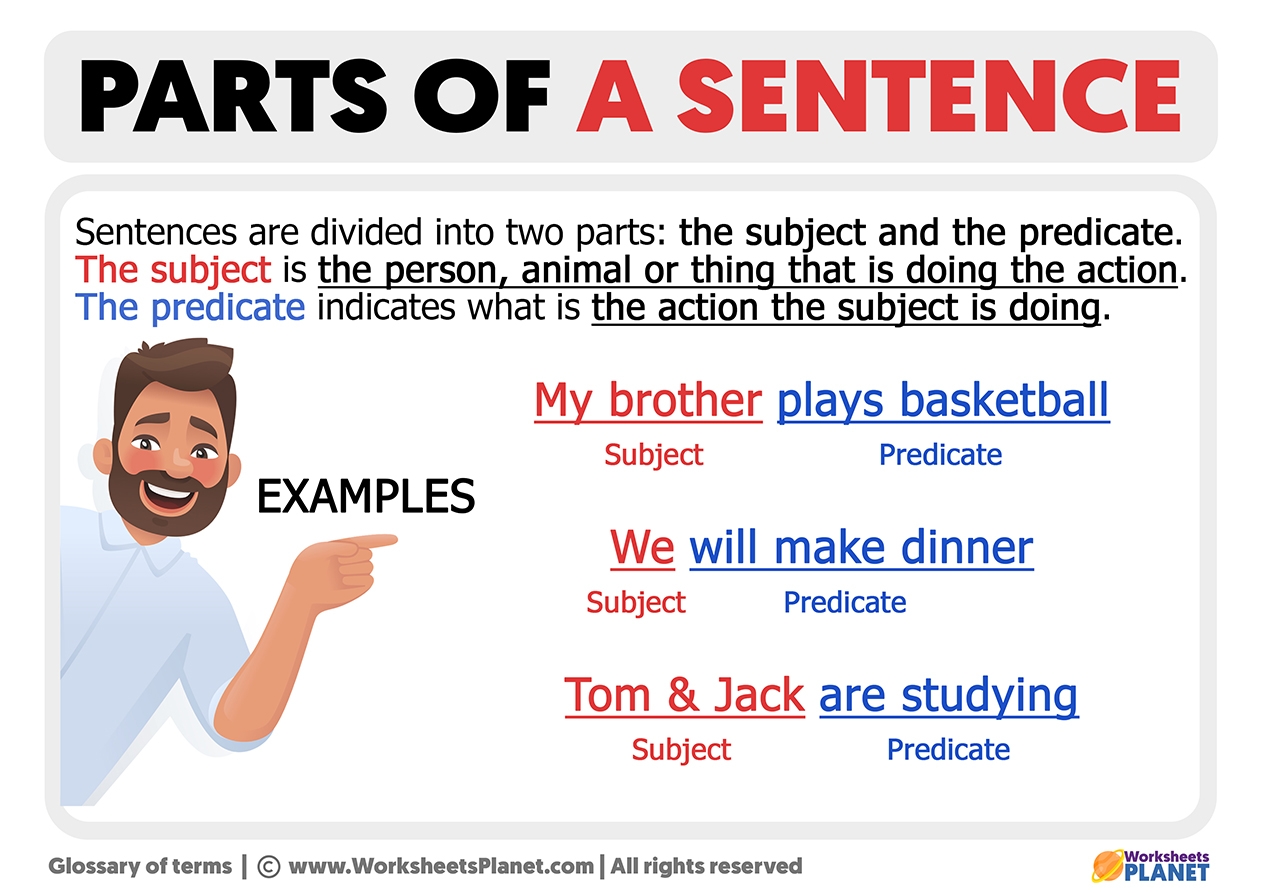
Sentences are made up of different parts that work together to convey meaning. Understanding the various components of a sentence is essential for effective communication. Here, we will explore some examples of sentence parts to help you grasp their importance in constructing coherent sentences.
1. Subject: The subject is the main noun or pronoun that performs the action in a sentence. For example, in the sentence “The cat chased the mouse,” “cat” is the subject.
2. Verb: The verb is the action or state of being in a sentence. It expresses what the subject is doing or being. In the sentence “She sings beautifully,” “sings” is the verb.
3. Object: The object is the noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb. In the sentence “John ate an apple,” “apple” is the object.
4. Adjective: An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. In the sentence “The red car is fast,” “red” is the adjective describing the car.
5. Adverb: An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It provides information about how, when, where, or to what extent something is done. In the sentence “She ran quickly,” “quickly” is the adverb describing how she ran.
Understanding how these sentence parts work together is crucial for effective communication. By mastering these components, you can create clear and concise sentences that convey your intended message accurately.
In conclusion, sentence parts play a significant role in constructing meaningful sentences. By identifying and using subjects, verbs, objects, adjectives, and adverbs effectively, you can enhance the clarity and coherence of your writing. Practice incorporating these examples of sentence parts into your sentences to improve your communication skills.