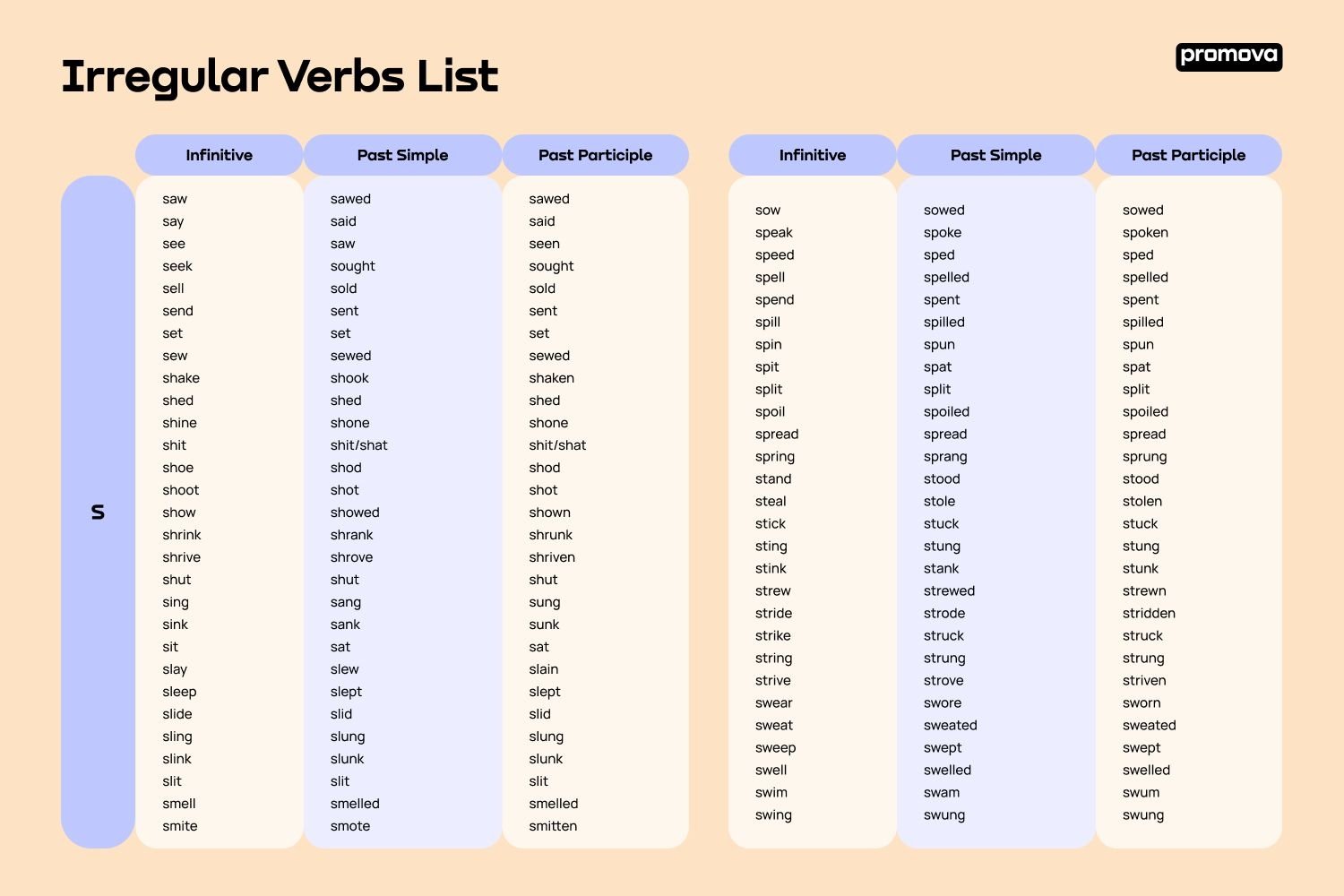
Irregular verbs are verbs that do not follow the regular pattern of conjugation in a language. In English, there are many irregular verbs that do not form their past tense or past participle by adding -ed to the base form. Instead, they have unique forms that must be memorized.
Learning irregular verbs can be challenging for language learners, as they often have to be memorized individually. However, mastering irregular verbs is essential for fluency in English and for understanding and communicating effectively in the language.
Examples of Irregular Verbs
Some common examples of irregular verbs in English include:
- Go – went – gone
- Eat – ate – eaten
- See – saw – seen
- Take – took – taken
- Drive – drove – driven
These irregular verbs do not follow the typical pattern of adding -ed to form their past tense and past participle forms. Instead, they have unique forms that must be memorized through practice and repetition.
It is important for language learners to regularly practice using irregular verbs in sentences to reinforce their correct usage and to build fluency in English. Reading and listening to native speakers using irregular verbs in context can also help learners become more familiar with their forms and usage.
While irregular verbs may seem daunting at first, with consistent practice and exposure to the language, learners can become more comfortable and confident in using them correctly. Remembering the irregular forms of common verbs will help improve overall language proficiency and communication skills.
In conclusion, irregular verbs are an important aspect of English grammar that require dedicated practice and study. By familiarizing oneself with the irregular forms of common verbs and using them in context, language learners can improve their fluency and communication skills. Continued exposure to irregular verbs through reading, listening, and speaking will help reinforce their correct usage and enhance overall language proficiency.