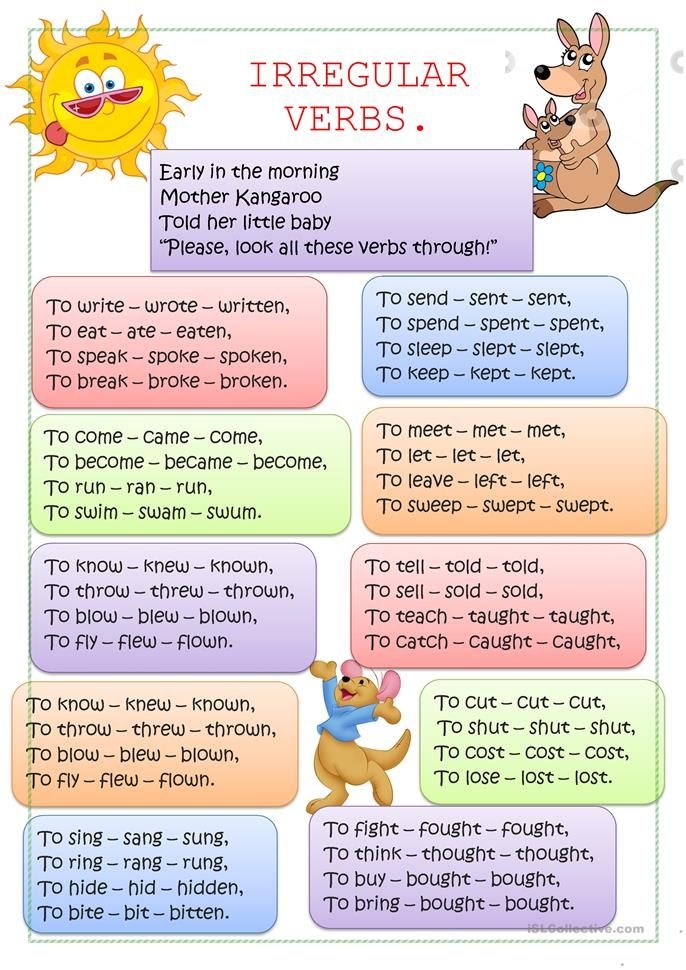
Irregular verbs are verbs that do not follow the regular pattern of adding -ed to form their past tense or past participle. Instead, they have unique forms that must be memorized. While regular verbs follow a predictable pattern, irregular verbs require more attention and practice to master.
English language learners often struggle with irregular verbs because of their unpredictable nature. However, mastering these verbs is essential for achieving fluency in English. Understanding and using irregular verbs correctly can greatly improve your speaking and writing skills.
Examples of Irregular Verbs
Some common examples of irregular verbs include:
- go – went – gone
- eat – ate – eaten
- see – saw – seen
- take – took – taken
- drive – drove – driven
These verbs have unique past tense and past participle forms that do not follow the regular -ed pattern. It is important to memorize these irregular forms and practice using them in sentences to improve your English language skills.
Irregular verbs can also change their base form in the present tense. For example, the verb “be” changes to “am,” “is,” and “are” in the present tense for different subjects. Understanding the various forms of irregular verbs in different tenses is crucial for effective communication.
One of the best ways to learn irregular verbs is through practice and repetition. Create flashcards, use online resources, and engage in conversations that allow you to use irregular verbs in context. The more you practice, the more comfortable you will become with using irregular verbs correctly.
In conclusion, irregular verbs play a significant role in the English language and mastering them is essential for language learners. By understanding the unique forms of irregular verbs and practicing their usage, you can improve your overall English language skills and communicate more effectively. Embrace the challenge of learning irregular verbs and watch your language proficiency grow.