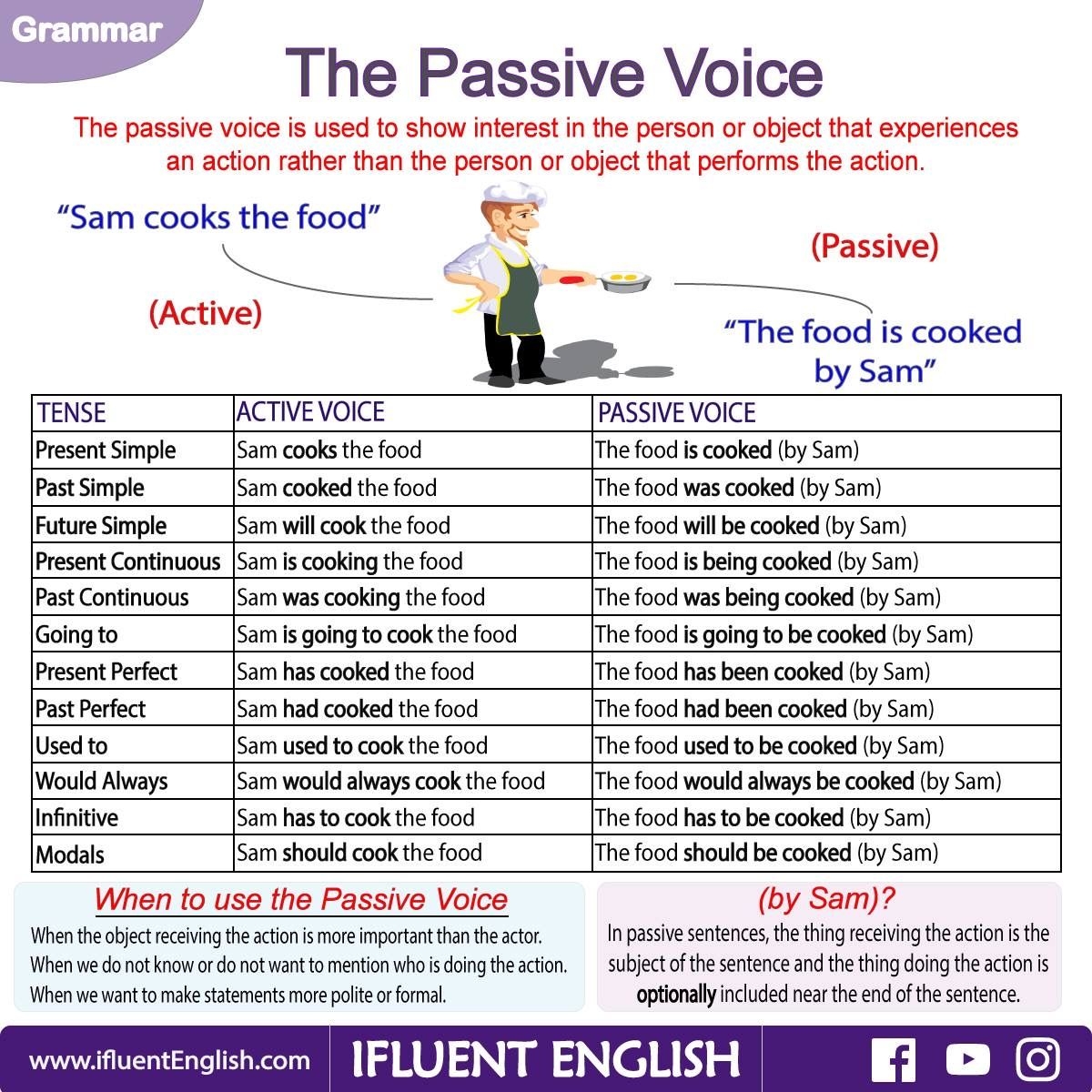
Passive sentences are a common grammatical construction in which the subject of a sentence is acted upon by the verb. This type of sentence structure is often used when the focus is on the action rather than the doer of the action. Understanding passive sentences can help improve your writing and communication skills.
Passive sentences can be identified by the use of a form of the verb “to be” (such as is, are, was, were) followed by the past participle of the main verb. For example, “The book was read by the student.” In this sentence, the book is the subject that is being acted upon by the student.
Passive Sample Sentence:
The cake was baked by my mom.
Passive sentences are often used in formal writing, such as academic papers or reports. They can also be used to shift the focus of a sentence from the doer of the action to the action itself. For example, “The project was completed ahead of schedule.” In this sentence, the emphasis is on the completion of the project rather than who completed it.
Passive sentences can also be used to avoid placing blame or responsibility on a specific person. For example, instead of saying “John broke the window,” you could say “The window was broken.” This can be useful in situations where it is not necessary or appropriate to identify the doer of the action.
However, it is important to use passive sentences judiciously. Overusing passive voice can make your writing sound awkward or unclear. It is generally recommended to use active voice whenever possible, as it is more direct and engaging for the reader. Passive sentences should be used when the focus is on the action or when the doer of the action is unknown or unimportant.
In conclusion, understanding passive sample sentences can help improve your writing skills and make your communication more effective. By knowing when and how to use passive voice, you can convey your message clearly and concisely. Practice incorporating passive sentences into your writing to add variety and depth to your work.