English grammar can be tricky, especially when it comes to tenses. Two of the most commonly used tenses in English are the present simple and past simple. These tenses are essential for everyday communication and are used to describe actions or states of being in the past and present.
Understanding the differences between the present simple and past simple tenses is crucial for effective communication in English. By mastering these tenses, you can convey information accurately and clearly in both spoken and written language.
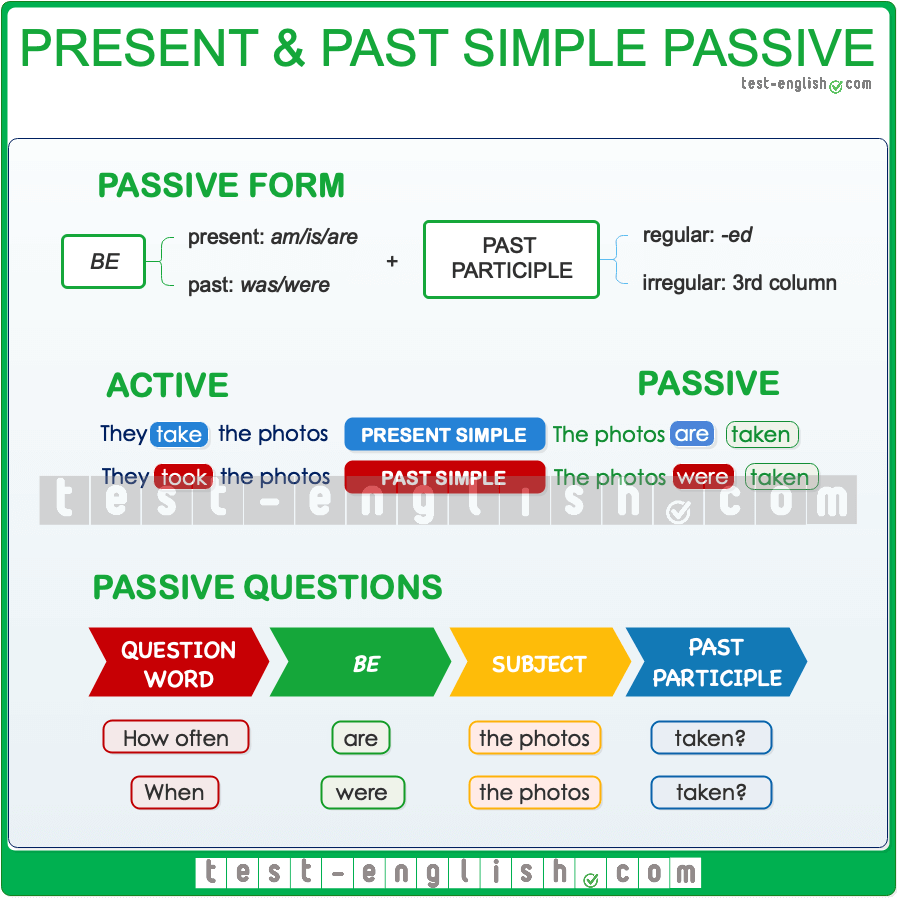
Present and Past Simple
The present simple tense is used to describe actions that are habitual, routine, or factual. It is formed by using the base form of the verb with ‘s’ or ‘es’ added for third-person singular subjects. For example, “She works in a bank” or “They go to school every day.”
On the other hand, the past simple tense is used to describe actions that were completed in the past. It is formed by adding ‘-ed’ to regular verbs or using the irregular verb form for irregular verbs. For example, “I walked to the store yesterday” or “She ate lunch at noon.”
When using the present simple tense, it is important to remember to use the correct verb form based on the subject. For example, “He reads books” uses the base form of the verb ‘read’ with ‘s’ added for the third-person singular subject ‘he.’ In contrast, the past simple tense requires the use of the past form of the verb to indicate that the action took place in the past.
Overall, mastering the present and past simple tenses is essential for effective communication in English. By understanding how and when to use these tenses, you can convey information accurately and clearly in a variety of situations. Practice using these tenses in everyday conversations and writing to improve your fluency and confidence in English.
In conclusion, the present simple and past simple tenses are fundamental components of English grammar. By understanding the rules and usage of these tenses, you can enhance your communication skills and express yourself more effectively in both spoken and written English.