Present Perfect vs Simple Past
When it comes to English grammar, the difference between present perfect and simple past can sometimes be confusing for learners. Both tenses are used to talk about past actions, but they are used in different contexts. Understanding when to use each tense can greatly improve your language skills.
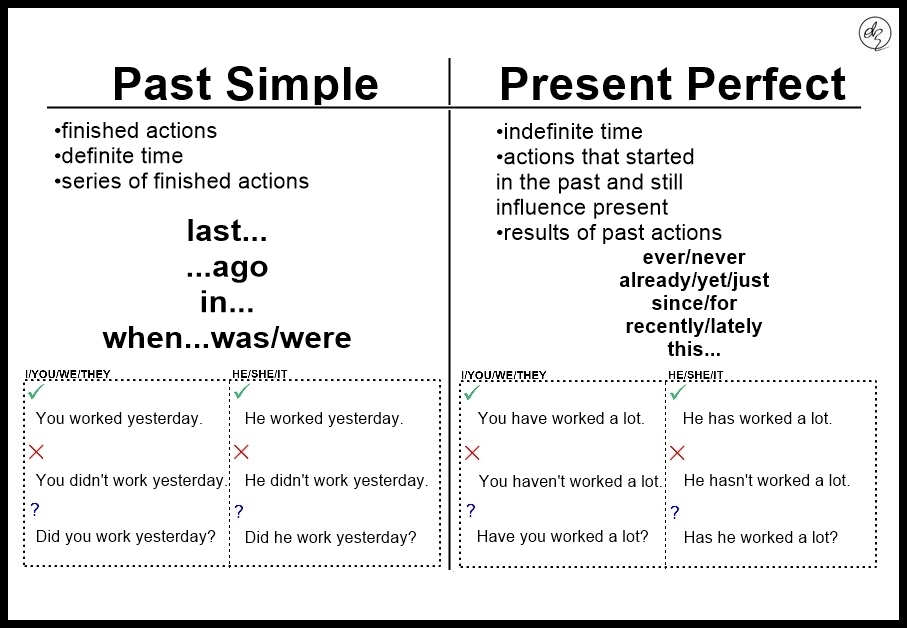
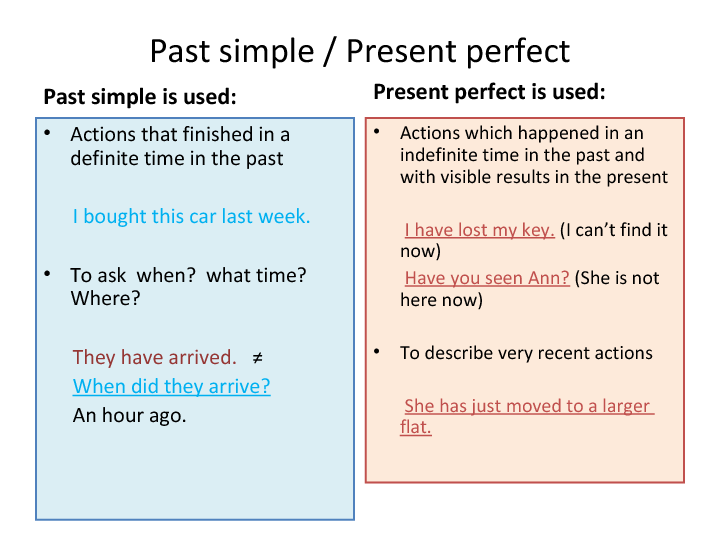
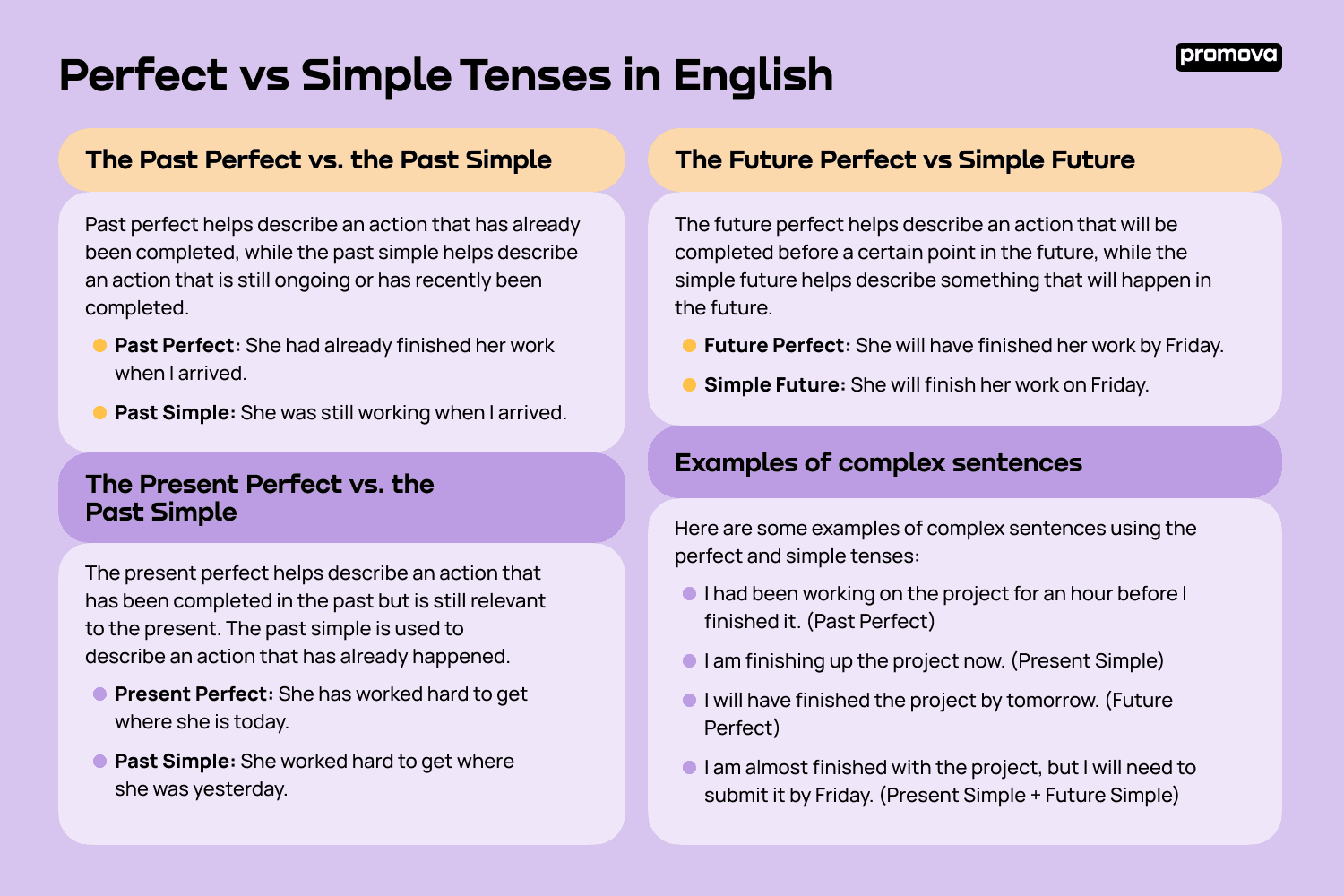
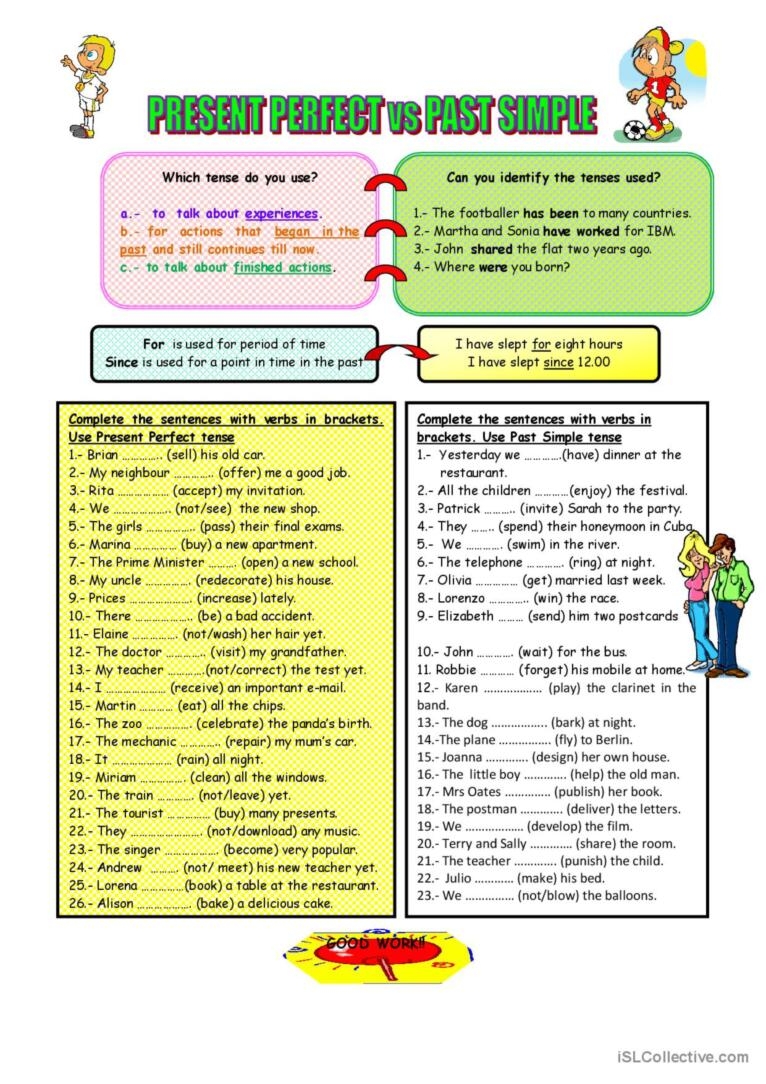
Present perfect is used to talk about actions that have been completed in the past but have a connection to the present. On the other hand, simple past is used to talk about actions that were completed at a specific point in the past. Let’s delve deeper into the differences between these two tenses.
Present Perfect vs Simple Past
Present perfect is formed by using the auxiliary verb “have” or “has” followed by the past participle of the main verb. For example, “I have visited Paris.” This tense is often used to talk about experiences, actions that have just been completed or actions that have relevance to the present moment.
On the other hand, simple past is formed by using the past form of the main verb. For example, “I visited Paris last year.” This tense is used to talk about actions that were completed at a specific point in the past and do not have a connection to the present.
Another key difference between present perfect and simple past is the use of time expressions. Present perfect is often used with time expressions such as “just,” “already,” “yet,” and “never.” Simple past, on the other hand, is used with time expressions such as “yesterday,” “last week,” and “in 1999.”
In conclusion, understanding the differences between present perfect and simple past is essential for mastering English grammar. By knowing when to use each tense and being able to recognize the appropriate time expressions, you can effectively communicate about past actions in English. Practice using both tenses in various contexts to improve your language skills.