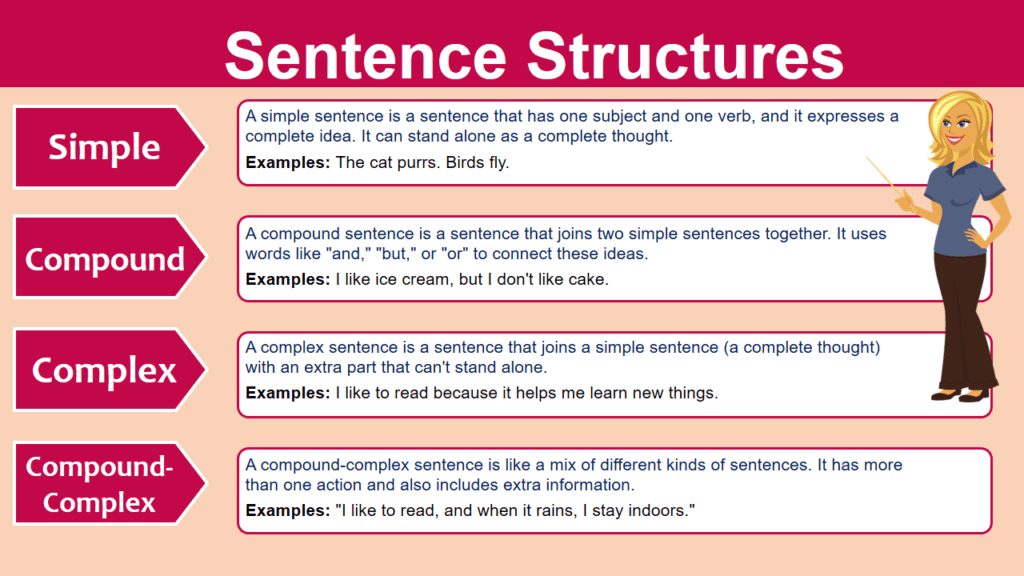
Sentence structure is a crucial element of writing that can greatly impact the clarity and effectiveness of your message. By understanding the basic components of a sentence and how they work together, you can create sentences that are clear, concise, and easy to understand.
Proper sentence structure involves arranging words in a logical order to convey meaning. A well-structured sentence typically consists of a subject, verb, and object. However, there are various ways in which sentences can be structured to convey different meanings and emphasize different elements.
Examples of Sentence Structures:
1. Simple Sentence: The dog barks loudly.
This sentence follows a basic structure with a subject (the dog) and a verb (barks) that express a complete thought.
2. Compound Sentence: The cat meowed and the dog barked.
A compound sentence consists of two independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction (and, but, or, so). In this example, the two clauses are “The cat meowed” and “the dog barked.”
3. Complex Sentence: While I was cooking dinner, the phone rang.
A complex sentence contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. The independent clause “the phone rang” can stand alone as a complete sentence, but the dependent clause “While I was cooking dinner” cannot.
4. Compound-Complex Sentence: The sun was shining, so we decided to go for a walk, but it started raining.
This sentence combines elements of both compound and complex sentences. It contains two independent clauses (“The sun was shining” and “we decided to go for a walk”) and one dependent clause (“but it started raining”).
Conclusion
Understanding sentence structure is essential for effective communication in writing. By mastering different sentence structures, you can convey your message clearly and engage your readers. Remember to vary your sentence structures to keep your writing interesting and engaging.