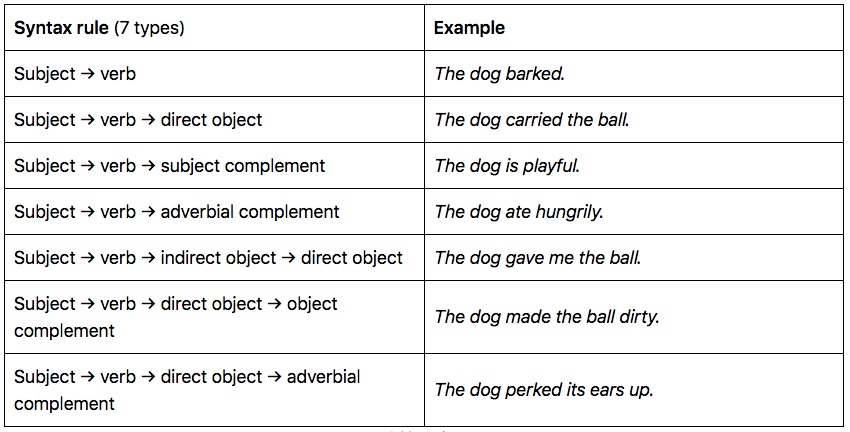
In linguistics, syntax refers to the rules that govern the structure of sentences in a language. These rules dictate how words can be arranged to form meaningful and grammatically correct sentences.
Understanding syntax grammar is essential for effective communication, as it helps us convey our thoughts and ideas clearly. By following the rules of syntax, we can ensure that our sentences are coherent and easily understood by others.
Examples of Syntax Grammar
1. Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) Sentence Structure:
In English, the most common sentence structure is Subject-Verb-Object. For example, “She (subject) eats (verb) an apple (object).” This order of elements is necessary for the sentence to make sense.
2. Agreement of Verb with Subject:
Another important rule of syntax grammar is the agreement of the verb with the subject in terms of number and person. For instance, “He (singular subject) goes (singular verb) to school” and “They (plural subject) go (plural verb) to school.”
3. Use of Articles:
Articles (a, an, the) play a crucial role in English syntax grammar. For example, we say “I have a car” to indicate that we have one car (indefinite article) and “The car is red” to refer to a specific car (definite article).
4. Placement of Adjectives:
In English syntax, adjectives usually come before the noun they describe. For instance, “The beautiful (adjective) flowers (noun) bloom in spring.” Placing the adjective after the noun would result in a different meaning or incorrect sentence structure.
5. Use of Punctuation:
Punctuation marks such as commas, periods, and question marks are essential for indicating the structure of a sentence. For example, “Are you going to the store?” conveys a question, while “She went to the store, bought groceries, and returned home.” shows a series of actions.
Understanding and applying syntax grammar rules enable us to communicate effectively and avoid misunderstandings. By following these examples and principles, we can construct clear and coherent sentences that convey our intended message.